In an era of increasing choices, healthcare facilities must evolve to meet the rising expectations...
Data Analytics in ASCs – Applying Data to Design
It all continued with a deeper dive and a second cup of coffee.
This article builds on our earlier piece, Data Analytics in ASCs – A Holistic View, where we uncovered how powerful data can be in shaping the success of ambulatory surgery centers. Now, we are zooming in to explore how those data points can go beyond operations and inform the design of ASCs. By gaining insights from historical precedents, patient experience, and feedback from clinical staff, we can translate analytics into smarter, more efficient, and patient-centered design decisions.
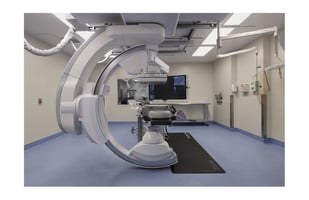
A primary metric with significant design implications is Patient Throughput - the speed and efficiency with which patients move through intake, pre-op, surgery, recovery, and discharge. By studying this data, architects and planners can identify high-traffic zones and flow bottlenecks, and adapt floor plans accordingly to improve circulation and minimizing downtime between procedures. For example, consolidating pre-op and recovery bays close to operating rooms, minimizing unnecessary circulation spaces, strategically pairing operating rooms to enable simultaneous use and preparation, and providing adequate interview stations to optimize waiting areas for peak periods can enhance patient flow and reduce unnecessary delays, thus improving revenue.

Staff Movement and Efficiency data such as travel distances and frequency of room access can directly inform spatial planning. When workflows are mapped using tools like spaghetti and bubble diagrams, they often reveal inefficiencies that can be corrected by more intuitive adjacencies and decentralized workstations. For instance, placing clean supply rooms closer to procedure areas or designing dual-access corridors can save steps and time, helping reduce staff fatigue and improve productivity. Similarly, analyzing supply flows supports more streamlined design. Understanding the lifecycle of sterile and soiled materials, restocking schedules, and maintenance needs allows designers to develop more efficient layouts.

A particularly valuable but often underutilized resource is Health Inspection Trend Data. By collecting and analyzing reports from past Department of Health and building inspections, teams can identify recurring deficiencies such as clearances, fire rated assemblies & stenciling, rated door labels etc. More importantly, patterns in inspector questions and comments help teams anticipate and proactively address compliance issues. This not only streamlines the inspection process but significantly reduces the chance of rework or rejected submissions, especially during sensitive project timelines.
Closely linked is the use of Regulatory Data Collection, which spans state health regulations, facility guidelines, accessibility codes, electrical and HVAC codes, and more. By organizing and referencing this collected data, teams can develop a comprehensive knowledge base to guide new designs. This allows for quicker design decisions, easier compliance reviews, and more effective training for junior staff.
To make this knowledge actionable, creating Architectural Checklists derived from historical projects is invaluable. By analyzing project timelines and deliverables ranging from schematic design to construction administration, teams can build comprehensive, phase-based checklists. These function as both task trackers and design guidelines, helping to avoid omissions, plan ahead, and maintain project momentum.
Analyzing Current Trends in Healthcare Design and Aesthetics is essential. Many clients today seek high-end, hospitality-inspired, or home-like environments in their ambulatory surgery centers, yet often operate within tight budget constraints. By using data to identify recurring preferences and priorities, designers can offer curated options that align with client aspirations while avoiding the pitfalls of overwhelming choices. This reduces time spent on back-and-forth iterations and helps clarify the project vision early.
Infection Control Metrics are also key to improving ASC design. Data on post-op infections, compliance with hygiene protocols, and airflow patterns can help guide decisions around room adjacencies, finish materials, and HVAC zoning.
Noise levels and acoustic data can inform the use of sound-absorbing materials and the placement of noisy equipment, particularly to protect recovery areas and staff workstations. Energy usage data over time can guide the selection of HVAC systems, medical equipment, lighting controls and sensor technologies to reduce utility costs without compromising performance.
With every dataset, whether from workflows, regulations, energy logs, or patient behavior, comes an opportunity to make smarter design choices. The integration of these insights transforms design of ambulatory surgery centers from a subjective process into an evidence-based practice.
What’s next?....
“Data Analytics in ASCs – Transforming Insights into Action”